Background:
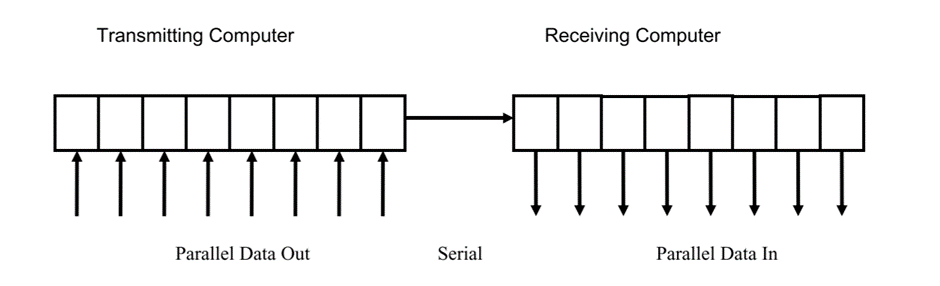
Serial communication (such as UART, SPI and other protocols) is widely used in modern applications because of its practicality over parallel. In serial communications, the data stored within a computer in clusters of bits, either bytes (8 bits at a time) or words (8/16/32 bits at a time), is decomposed into its individual bits before being transmitted one bit at a time to another computer. In serial data transmission the data is sent 1 bit at a time from a parallel in/serial out shift register to a serial in/parallel out shift register.
At its simplest, it is like:
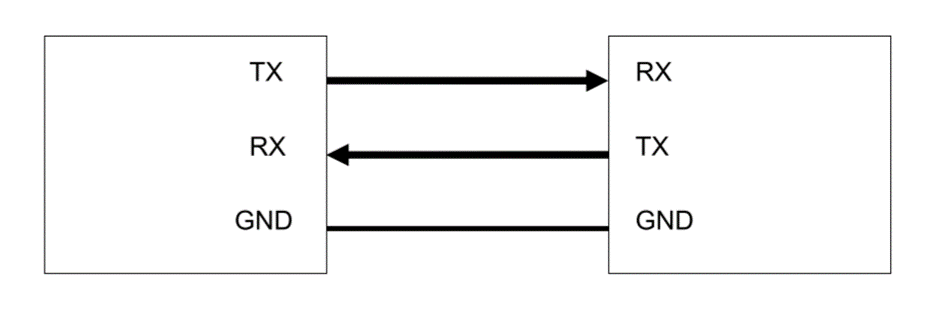
- TX: Transmit line.
- RX: Receive line
- GND: Common ground.
Outline:
UART:
UART has one connection in each direction + common Gound. Meaning, it is often called “2-wire serial”. And, it is most used for “low volume transmissions”.
Key info: “UART is a 2-wires protocol (send, receive and ground)”
Pros and Cons of UART:
Pros:
- UART is easy to implement, hardware is not complex.
- Widely used, many applications use it.
Cons:
- UART is inefficient as it requires min of 2 extra bits to be transmitted with every 8-bits of data.
- Only 2 devices can be connected using UART to communicate.
UART data format:
- Transmitter:
Shift the parallel data onto the serial line using the transmitter’s clock and adds start, end and parity bits.
| Start bit (1 bit) | Data bits (5-8 bits) | Parity (1 bit) | Stop bit (1-2 bits) |
- Start bit: Indicates the beginning of the data word.
- Data bits: The actual data to be transmitted.
- Parity but (optional): For error correcting (Even or Odd).
- Stop bit: Indicates the end of the data word.
NB: Baud rate (number of symbols per second) must be defined at the same rate beforehand in the transmitter and receiver.
- Receiver:
Extracts the data using its own clock and converts the serial data back to the parallel form after stripping off the start, stop and parity bits.
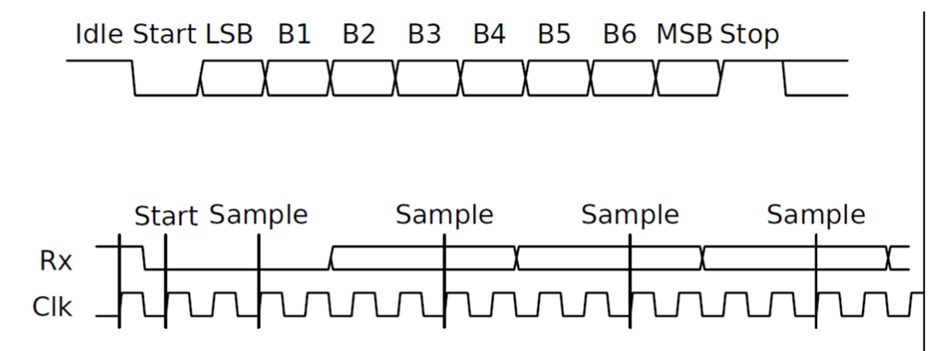
Most UARTs uses 16 x Clock cycle. Take a sample at every 16 x Clock tick. Therefore, incoming signal must be around 16 times slower than the clock.
Key info: “Want something robust, bulletproof and everyone uses? Use UART”
Conclusion:
- Serial communication is widely used in modern applications because of its practicality over parallel.
- UART is a 2-wires protocol – send, receive and ground.
- It is easy to implement but inefficient as it requires min of 2 extra bits to be transmitted with every 8-bits of data.
- Only 2 devices can be connected using UART.
- UART data format: start bit, data bit, parity bit(s) and stop bit.
- Receiver uses its own clock to pick up data from the receive line.
- UART is robust, bulletproof and everyone uses.